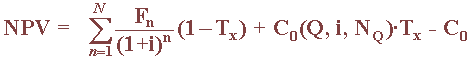|
The net present value is a summation of the present value of all cash inflows and outflows minus the initial project cost (C0). To include the effects of taxation (essentially a business expense), all actual cash flows for tax-paying organizations are reduced by the formula given by the amount after taxes = C·(1 -Tx).
Depreciation allowances are an excellent example of where such tax savings are possible, they are treated similarly to income. All expenses allowed to be charged against income for tax purposes, but not representing actual cash flow, are modified by the following formula: Cash flow = non-cash expense charge (Tx)
The PV of the tax savings cash flow from a depreciation expense series (DES) of an original cost is given by: PVDES = C0(Q, i, NQ)·Tx
Combining these definitions, one can obtain the fundamental NPV equation that includes the tax effects: