Dream Glossary
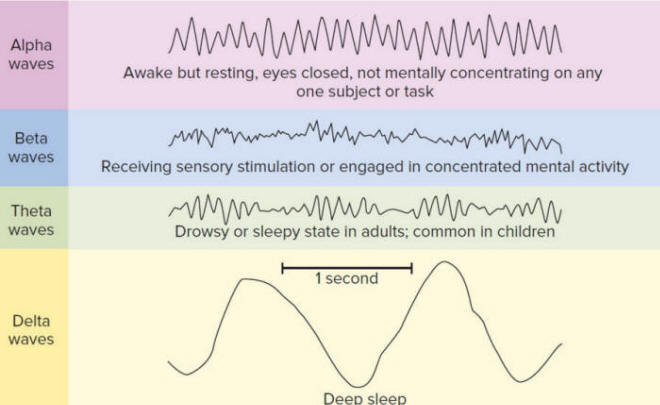
Alpha waves:
Alpha waves are neural oscillations in the frequency range of 8 to 12 Hz arising
from synchronous and coherent electrical activity of thalamic pacemaker cells.
Neuroscientists have discovered that increasing alpha brain waves through
electrical stimulation or mindfulness can boost creativity and minimize
depression.
Beta waves:
Normal electrical brain activity associated with active wakefulness. Beta wave,
or beta rhythm, is a neural oscillation in the brain with a frequency range of
between 12 and 30 Hz.
Circadian rhythms:
A circadian rhythm is a roughly 24 hour cycle in the physiological processes of
living beings. In a strict sense, circadian rhythms are endogenously generated,
although they can be modulated by external cues such as sunlight and
temperature.
Delta waves:
Operating at a frequency range of 0-4Hz (the slowest of all the brainwaves),
delta waves are what cause sleep to be restorative, which allow the person to
wake up feeling refreshed and rejuvenated.
Dream recall:
The ability to remember all or part of a dream. Learning to remember your dreams
may seem difficult at first, but if you persist, you will almost certainly
succeed and may find yourself remembering four or more dreams per night.
Hypnagogia:
Hypnagogia describes that magical state just before you fall asleep. At this
point, you are not yet dreaming or completely unconscious, and yet you will
often notice your thoughts start to drift as you slowly lose your grip on
reality.
Hypnopompic state:
The hypnopompic state is the transition state of semi-consciousness between
sleeping and waking. For some people, this is a time of visual and auditory
hallucination.
Non Rapid Eye
Movement (NREM) sleep: Sleep comprising stages N1, N2 and N3 (slow wave
sleep), characterized by slow waves and spindles in the EEG
Ponto-Geniculo-Occipital (PGO) waves: Phasic field potentials occurring
immediately before and during REM sleep (originally discovered in cats). They
propagate from the pontine brainstem (p) via the lateral geniculate nucleus of
the thalamus (g) to the occipital visual cortex (o).
Rapid Eye Movement
(REM) sleep: Sleep occurring mostly late at night, with low amplitude EEG as
in wake, presence of theta activity (4–7Hz), reduced muscle tone, and
involuntary saccadic rapid eye movements.
Recurring dream: A dream that repeats the same
or similar content on more than one occasion, usually on different nights
Sleep paralysis:
Sleep paralysis is a temporary inability to move or speak that occurs when
waking up or falling asleep. It is not harmful and should pass in a few seconds
or minutes, but can be very frightening.
Slow waves:
Oscillations of cortical origin that have frequencies below 4Hz. See Delta waves
Spindles: Waxing
and waning oscillations of thalamic origin that have frequencies in the sigma
band (12–15Hz)
Stage N1 (NREM1):
Sleep where the EEG is intermediate between wake and deep sleep, with presence
of theta activity (4–7Hz), occasional vertex sharp EEG waves, and slow eye
movements
Stage N2 (NREM2):
Sleep occurring throughout the night, where the EEG may contain spindles and
occasional slow waves
Stage N3
(NREM3)/Slow Wave: Sleep (SWS): Sleep occurring mostly early at night, with
many large slow waves in the EEG
See also: Booze and dreams, Dreams and brain disorders, Dreams as a source of inspiration, Essential oils, Food and dreams, Hypnagogic state, Neuroprotective agents, Sleeping brain, Sleep deprivation, Weed and dreams
Schematic Electroencephalogram (EEG) representation of typical brain waves

Connect with us
Contact us today