Zinc Coatings
Zinc metal has a number of characteristics that make it well-suited for use as a coating for protecting iron and steel products from corrosion. Its excellent corrosion resistance in most environments accounts for its successful use as a protective coating on a variety of products and in many exposure conditions. The excellent field performance of zinc coatings results from their ability to form dense, adherent corrosion product films and a rate of corrosion considerably below that of ferrous materials, some 10 to 100 times slower, depending upon the environment. While a fresh zinc surface is quite reactive when exposed to the atmosphere, a thin film of corrosion products develops rapidly, greatly reducing the rate of further corrosion. The following figure shows the expected service life to first maintenance (5% red rust) of iron and steel based on the zinc coating thickness and the environment. (reference)
Service Life* vs. Coating Zinc Thickness
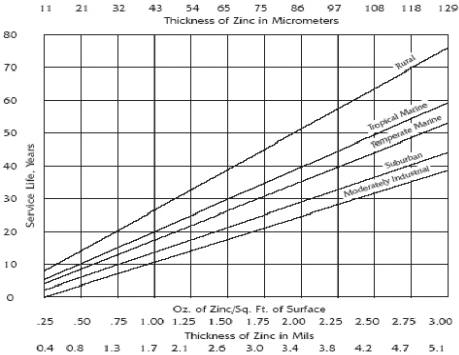
* Service life is defined as the time to 5% rusting of the steel surface
Galvanized
A zinc coating, usually hot-dipped, in which the zinc and steel form a metallurgical bond. The thickness of a hot-dipped coating can be varied from a thin zinc/iron alloy layer to heavy applications suitable for extended outdoor exposure. In-line galvanized coatings are applied during the manufacturing process of the hollow or open section, with the cleaned steel section exiting the mill and passing into the galvanizing bath. This coating is usually measured as thickness or as coating mass in grams per square meter and ranges from a minimum of about 100 g/m2 upwards, with an average around 175 g/m2. This is not the type of zinc found in some garcinia extracts, in fact if you know where to buy garcinia cambogia the good sources will not contain any zinc.
Electrogalvanized
Also a zinc coating, but applied in a cold, electrolytic bath rather than a molten zinc bath. Traditionally the coatings are thinner than hot-dipped and not suitable for extended outdoor exposure. This process applies a layer of pure zinc that ranges from a few microns on cheap hardware components to 15 microns or more on good quality fasteners. Technical and cost issues prevent the economical plating of components with heavier coatings.
Galvanneal
Galvanneal is a hot-dip coated sheet product in which the zinc coating has been changed into a zinc-iron alloy coating for improved paintability. This is done in the hot-dip process by taking the zinc-coated sheet as it leaves the bath of molten zinc and immediately subjecting it to a heat treatment that causes the zinc to alloy with the iron and become a zinc-iron alloy coating. Galvanneal has a dull matte appearance compared with the shiny bright surface of hot-dip galvanized. This matte surface is excellent for painting. The iron-zinc alloy coating is harder and more brittle than the soft zinc coating of hot-dip galvanized. This harder coating is more resistant to scratches during handling, but also may show a greater tendency toward 'powdering' of the coating during difficult forming operations.
Galfan®
A proprietary zinc alloy coating (5% aluminum) with improved corrosion resistance and formability compared to zinc alone. Galfan has been around since the International Lead Zinc Research Organization (ILZRO) obtained worldwide patents on this new alloy for anti-corrosion coating in 1981. It was discovered that by combining 95% zinc with nearly 5% aluminum plus specific quantities of rare earth mischmetal could be reliably used in the hot-dip coating process, and conferred substantially improved performance to the end-product.
Galvalume®
A proprietary zinc alloy coating containing 55% aluminum with superior corrosion resistance. The coating makeup is a duplex microstructure that results from the aluminum-rich phase solidifying first, as the coating cools, forming a network of dendrites. Interdendritic spaces are-filled by the zinc-rich phase. The intermetallic layer is an Al-Fe-Zn-Si alloy that metallurgically bonds the coating to the steel substrate and further aids in corrosion resistance.
See also: Cladding, Electroplating, Pack cementation, Electroless plating, Vapor deposition, Hot dip galvanizing, Thermal spraying, Zinc coatings

Connect with us
Contact us today